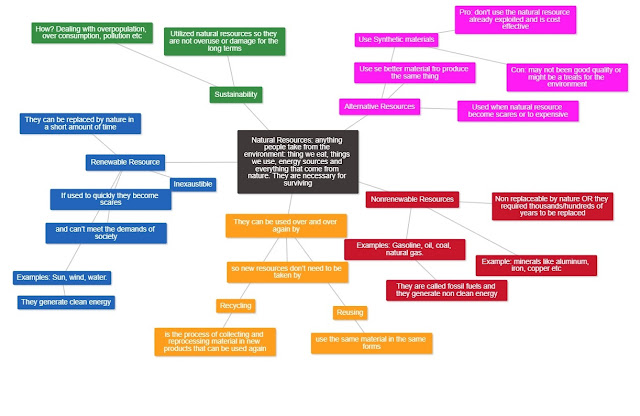
Activity 3.3.1 Air Pollution Core Activity.
Air Pollution Basics Air pollutant are emitted from both natural sources and anthropogenic emission (Freedman, 2018). These pollutants if reach a certain amount can be dangerous for human health and cause severe damage to people. The basics air pollutant are: Sulfur, Nitrogen and Hydrocarbon and Volatile Organic Compound. Sulfur Pollutants The main Sulfur pollutant are Sulfur Dioxide, or SO2, and Hydrogen Sulfide, or H2S. SO2 and H2S react with Oxygen once they are emitted in the atmosphere. They both become oxidized and this process create another substance called Sulfate. Sulfate, or SO4^2- has a negative charge. Since Sulfate has a negative charge, it reacts very easily with element with positive charge creating various compounds. In fact, element with opposite charge attract each other. Atmospheric sulfate occurs as tiny particles like Ammonium Sulfate (NH4)2 SO4 and Ammonium Nitrate (NH4NO3). Sulfur gasses are emitted in nature, for example by Volcanoes. However, human S...